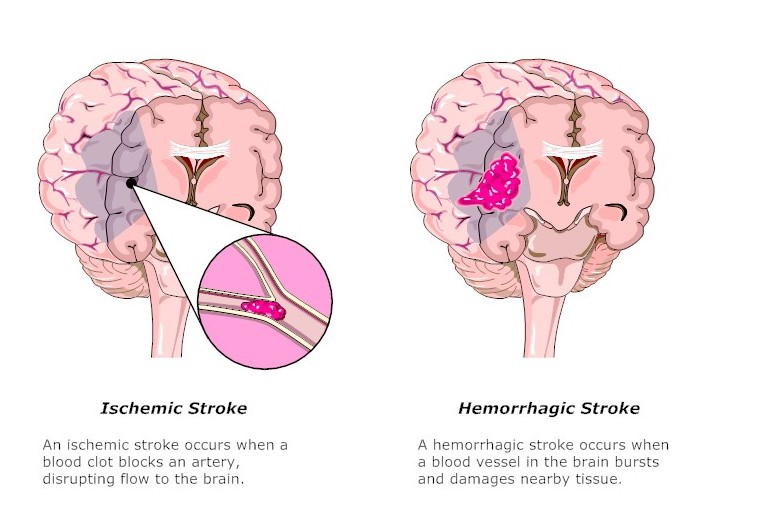
Stroke is usually one of the most daunting diagnosis given to patient. This can be caused by either secondary to lack of blood flow to certain region within the brain resulting in an ischemic stroke or when a blood vessel ruptures resulting in a hemorrhagic stroke.
Ischemic strokes can occur secondary to progressive narrowing of both intracranial and/or extracranial arteries or secondary to a sudden occlusion of a blood vessel that may arise from either a plaque or blood clot that can be from many origins. These people may have history of smoking, obesity, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, irregular heart rhythms, diabetes or other standing disease that increase their risk for stroke.
Hemorrhagic stroke can occur secondary to uncontrolled high blood pressure, aneurysm rupture, arteriovenous malformation or cavernoma rupture or trauma.
Stroke becomes more common as we age, however there is a lot that we can do to prevent a major stroke from occurring by simply managing our diet and overall health. It is also important to note that after a stroke, people tend to recover a good portion of lost functionality overtime, thus continued follow up with treatment is critical to optimize quality of life.
Acute stroke symptoms:
- Experienced symptoms depend on the region of the brain that is affected by the stroke.
- In the acute setting the symptoms are typically sudden and can have rapid progressive worsening, thus it is critical that you present to the nearest hospital or call for help.
-
Some common symptoms:
- Numbness
- Weakness
- Facial droop
- Slurred speech
- Confusion
- Changes in vision: loss of vision or double vision
- Balance and coordination difficulty
- In the acute setting it is essential that present to the nearest hospital as you will benefit from an immediate evaluation and may qualify for life saving treatments.
Diagnostic workup:
- Imaging: MRI, CT scan, Carotid duplex, MRA and CTA
- Cardiac workup: echocardiogram, EKG and/or Holter monitor
- Autoimmune workup and genetic workup in select group of patient
- Lipid panel
Treatment
- Treatment is geared towards prevention of a repeat stroke and recovery of lost functions.
- Treatment modalities:
- Patient education
- Rehabilitation with physical, occupational and speech therapy.
- Identification and treatment of risk factors such as hypertension, irregular heart rhythem, aneurysms, high cholesterol, blood clots, etc.
- Life style changes:
- Cessation of smoking
- Decrease alcohol consumption
- Weight loss
- Improve sleep hygiene
- Implementation of daily aspirin
Other cerebrovascular disorders:
- Intracranial aneurysm
- Arteriovenous malformation
- Cavernomas
- Cerebral venous Thrombosis
PNP will collaborate with leaders in the field of stroke across all major hospital to provide you with the best care that you deserve.